This is a follow-up to the previous post on Mobile Lifecycle metric Launches. If you have not read the post on launches, please go through the link before you get to the subject. As said during the previous post, helpx link to compare the metrics is redirecting to generic visits documentation (Helpx: https://helpx.adobe.com/in/analytics/kb/compare-visits-and-mobile-app-launches.html) and I personally don’t think that the points to compare the visits and mobile app launches is absolute in the link here.
There are 4 factors to be weighed when we compare the said metrics.
- Lifecycle session timeout [Already explained during the previous post]
- Foreground time [Already explained during the previous post]
- Background time [Already explained during the previous post]
- Visits increment conditions [12 Hours of continuous activity or 30 minutes of inactivity or 2500 hits or 100 hits in 100 seconds]
For the comparison, we also presume that Server Calls are not triggered over the background duration.
Visits equals Launches
Visits will be equal to launches on the below scenarios.
1. Application is launched without any continuation to the previous session and is in the foreground only with visits increment conditions were not met.
Launches = 1 (Triggered on application open) and Visits = 1 (Counted along with launches during application open).
2. Application is launched without any continuation to the previous session, foregrounded back from the background and visits increment conditions were not met. The key note here is that lifecycle session timeout is set to lesser than or equal to 30 minutes and the backgrounded time period is less than the lifecycle session timeout.
Launches = 1 (Triggered on application open) and Visits = 1 (Counted along with launches during application open).
3. Application is launched without any continuation to the previous session, foregrounded back from the background and visits increment conditions were met. The key note here is that lifecycle session timeout is set to lesser than or equal to 30 minutes and the backgrounded time period is more than the lifecycle session timeout.
Launches = 2 (Triggered on application open and during the foreground because backgrounded time period is more than the lifecycle session timeout) and Visits = 2 (Counted along with launches during application open and when visits increment conditions were met).
4. Application is launched without any continuation to the previous session and foregrounded back from the background. The key note here is that lifecycle session timeout is set to more than 30 minutes and the backgrounded time period is more than the lifecycle session timeout.
Launches = 2 (Triggered on application open and during the foreground because backgrounded time period is more than the lifecycle session timeout) and Visits = 2 (Counted along with launches during application open and during the foreground because the session was inactive for more than 30 minutes i.e. Visits increment conditions to be met always).
5. Application is launched, crashed and reopened with visits increment conditions were met.
Launches = 2 (Triggered on application open and reopen after crash) and Visits = 2 (Counted along with launches during application open and when visits increment conditions were met).
Visits greater than Launches
Visits will be greater than launches on the below scenarios.
6. Application is launched without any continuation to the previous session and is in the foreground only with visits increment conditions were met.
Launches = 1 (Triggered on application open) and Visits = 2 (Counted along with launches during application open and when visits increment conditions were met).
7. Application is launched without any continuation to the previous session, foregrounded back from the background and visits increment conditions were met. The key note here is that lifecycle session timeout is set to lesser than or equal to 30 minutes and the backgrounded time period is less than the lifecycle session timeout.
Launches = 1 (Triggered on application open) and Visits = 2 (Counted along with launches during application open and when visits increment conditions were met).
8. Application is launched without any continuation to the previous session and foregrounded back from the background. The key note here is that lifecycle session timeout is set to more than 30 minutes and the backgrounded time period is less than the lifecycle session timeout.
Launches = 1 (Triggered on application open) and Visits = 2 (Counted along with launches during application open and during the foreground because the session was inactive for more than 30 minutes i.e. Visits increment conditions to be met always).
Visits lesser than Launches
Visits will be lesser than launches on the below scenarios.
9. Application is launched without any continuation to the previous session, foregrounded back from the background and visits increment conditions were not met. The key note here is that lifecycle session timeout is set to lesser than or equal to 30 minutes and the backgrounded time period is more than the lifecycle session timeout.
Launches = 2 (Triggered on application open and during the foreground because backgrounded time period is more than the lifecycle session timeout) and Visits = 1 (Counted along with launches during application open).
10. Application is launched, crashed and reopened with visits increment conditions were not met.
Launches = 2 (Triggered on application open and reopen after crash). Visits = 1 (Counted along with launches during application open).
Summary
Below is the quick lookup table for the ideal scenarios if we group the above discussed topics.
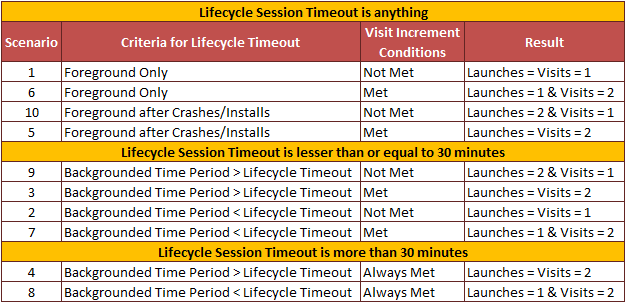
I have described the above list as ideal scenarios because the scenarios in the real world will still differ. Example, for scenario 10, if crashes/installs occur more than once within the 30 minutes time interval, launches would be greater than 1 (Not supposed to be 2 as said in the table) or if visits increment conditions were met more than once in the scenario 3, then visits will be greater than 2 making the scenarios void. However, the above list will provide a fair understanding on how launches and visits operate alongside variations which are significant when comparing the metrics. Happy comparing!






